- Demand For Money And Real Interest Rate Definition
- Demand For Money And Real Interest Rate Include
- Money Demand And Real Interest Rate
- Demand For Money And Real Interest Rates
The money demand curve is downward sloping, i.e., the demand for holding money increases with decrease in interest rates. The short-term interest rate (i) is determined by the equilibrium of the supply and demand for money. If the interest rates are above the equilibrium, there is excess supply of money.
Let us make an in-depth study of the linking variables between interest rate and income.
- If the demand for money depends positively on real income and depends inversely on the nominal interest rate, what will happen to the price level today if the central bank announces (and people believe) that it will decrease the money growth rate in the future, but it does not change the money supply today?
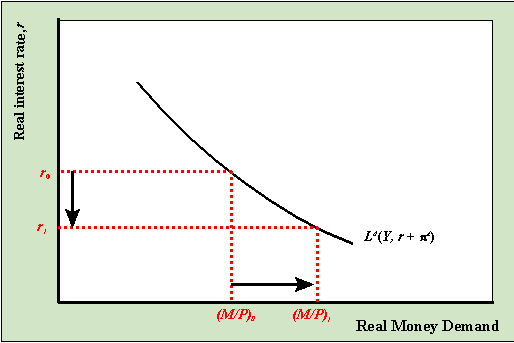
- Figure 18.5 Effects of an Increase in Real GDP. At the original interest rate, i$′, real money demand has increased to level 2 along the horizontal axis while real money supply remains at level 1. This means that real money demand exceeds real money supply and the current interest rate is lower than the equilibrium rate.
Introduction:
The interest rate and income are linking variables transmitting changes from the monetary sector to the goods sector and from the goods sector to the money sector. We now examine this relationship in more detail and analyse the concept of general equilibrium in the whole economy, consisting of the goods and money sectors.
Fig. 6.1 is a summary of equilibrium in the two sectors. The IS and LM curves represent the conditions that have to be satisfied in order for the goods and money sectors, respectively, to be in equilibrium. Now our task is to determine how these markets are brought into simultaneous equilibrium. For simultaneous equilibrium, interest rates and income levels have to be such that both goods market and money market are in equilibrium.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
That condition is satisfied at the point E in Fig. 6.1 which is the point of general equilibrium. This occurs at one combination of real income and the interest rate re and Ye and with this combination of income and interest rate there is no tendency for anything to change; individuals are in equilibrium in their allocation of wealth among different assets, and in their allocation of output among different uses.
Even though we are not concerned with the problem of economic dynamics, it is nevertheless important to understand the economic forces generated in this equilibrium, which tend to bring the system back to equilibrium.
Fig. 6.2(b) represents the equilibrium conditions for the goods and money sectors. Fig. 6.2(c) shows the money sector from which the LM curve in Fig.6.2(b) is derived and Fig 6.2(a) shows the desired investment schedule which together with the consumption function (not shown here) was used to derive the IS curve in Fig 6.2(b).
Point A shows the combination of real income (Y2) and interest rate (re) , respectively, which represents general equilibrium for the economy. At point A in the money sector, the quantity of money demanded shown by the demand curve Y2 is equal to the quantity of money supplied. At the interest rate re, desired investment is equal to IA – this is shown in Fig. 6.2(a). As point A is on the IS curve, we know that saving generated by a real income of Y2 is equal to IA, because every point on the IS curve represents a situation in which saving is equal to desired investment.
Let us consider point B in Fig. 6.2(b) which shows the combination of real income and interest rate Y2 and rB, respectively. We want to know what forces will be generated when the economy found itself in the situation represented by point B, and how these forces will work to bring the economy back to equilibrium. We know that at point B neither the goods nor the money sector is in equilibrium, because point B, is off both the IS and LM curves. Thus, something will have to change in both sectors.
In the money sector 6.2(c), we can see that at the combination of income and interest rate represented by point B, the quantity of money demanded is less than the quantity of money supplied. Individuals will try to re-allocate their wealth from money to bonds, thus pushing interest rate down. The arrow pointing down at B represents this tendency.
At panel 6.2(a), we see that at the interest rate rB, desired investment is IB. However, at real income Y2, saving is equal to IA, because we assume that S is a function of real income only; thus at point B, S > IB. Hence in the goods sector, point B represents a situation in which AD < Y. Given our present assumption about the effects of a disequilibrium in the goods sector, S > (desired) I will tend to reduce output (real income).
The arrow pointing to the left at B represents this tendency. (According to our assumptions about the goods sector disequilibrium, this only affects output, not the price level and as such it does not affect the LM curve).
The initial forces generated in disequilibrium have further repercussions on the whole economic system. The fall in the interest rate generated by excess supply of money will affect desired I =f(r). The fall in real income F generated by S > I (desired) in the goods sector will affect the demand for money, which is a function of real Y only. As the interest rate falls, desired I rises, reducing S > I (desired). As real Y falls, the demand for money and the interest rate fall, strengthening the effects mentioned above. All of this will continue until point A is reached — equilibrium point, in Fig. 6.2.
Disequilibrium and Dynamics in the Goods and Money Market:
Equilibrium is said to be a stable one when economic forces tend to push the market towards it. Fig. 6.3 shows that the general equilibrium described here is indeed a stable one. To show this, we consider all the points to the left of the IS curve, like point A where interest rate r1 and the level of Y1 are too low for equilibrium to be achieved in the real sector. This means that the total value of output is less than the demand.
In this situation, businesses find their inventories run down involuntarily and so act to increase output which pushes up Y. For all points to the left of the IS curve, there is an excess demand for goods and thus there is pressure on income to rise. Similarly, tor all points to the right of the IS curve, there is excess supply of goods and there is pressure on Y to fall.
Now we consider points above the LM curve, like point B. At this point, with the level of Y, OY1, the interest rate is too high for money market equilibrium to be achieved. This means that the supply of money exceeds the demand for money and so downward pressure is exerted on the interest rate. This is true for all points above the LM curve, as shown in Fig. 6.3 and it is also true that upward pressure will be exerted on interest rates at all points below the LM curve as there is excess demand for money.
The direction of the pressure being exerted on incomes and interest rates in the four quadrants are indicated by arrows in Fig. 6.3. At any disequilibrium point, such as C, economic forces will be pushing the market towards the general equilibrium position.
Shifting the IS and LM Curves:
Having analysed equilibrium in the two sectors, it is useful to examine how changes in behaviour will affect the two variables in which we are interested at present — real income and interest rate. There are four behavioural functions that determine equilibrium in the two sectors – the investment function and consumption function and the supply of money function and the demand for money function.
These functions were used to derive the IS and the LM curves and thus the behaviour represented by these functions is held constant along the IS and LM curves. A change is behaviour can be represented by a shift in these functions. Such shifts will result in the shift of the IS or LM curves, or, both.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Let us start from a situation of general equilibrium as shown by point A in Fig. 6.4. This is an equilibrium for that set of behavioural functions which underlies the derivation of the IS and LM curves intersecting at A. We now assume that for some reason, desired expenditures increase. For example, suppose there is an increase in desired investment at all interest rates (a shift in the investment function) or a rise in desired consumption at all income levels (a shift in the consumption function). These changes can be represented by a shift of the IS curve from IS to I’S’.
Now the economy is no longer in equilibrium at A because the goods sector now represented by I’S’ is no longer in equilibrium. However, the money sector is still in equilibrium as there is no change in the behaviour of the functions which affect money sector. We know that with the new IS curve, point A represents a situation in which desired expenditures are greater than total output (or I > S ). This will lead to an increase in Y.
As real Y rises, point A no longer represents equilibrium in the money sector either, because the increase in real Y affects the quantity of money demanded and thus equilibrium in the money sector will also change, though has been no behavioural change in the money sector (and hence the LM curve does not shift; there is a movement along the curve). The rise in the interest rate will’ have effects on desired I and on real Y.
This process will continue until a new equilibrium is reached at B with interest rate at rB and real income at YB. At B, both the money and goods sectors are in equilibrium. It may be pointed out here that if the shift in desired expenditures or AD had not affected the interest rate, real income would have changed from YA to Yc, which is equal to the initial change ‘in AD x the multiplier. This would be true if the LM curve is horizontal. Real Y only rises to YB because some of the initial increase in AD is offset by the effect of the rise in the interest rate on desired I, called the ‘crowding-out effect’.
A shift of the LM curve can occur because of a change in the demand for money or in the supply of money. An increase in the supply of money or a decrease in the demand for money can be represented by a shift of the LM curve to the right. To examine the effect of such changes, let us again start from a position of equilibrium at point A in Fig. 6.5. Assume there is an increase in the supply of money brought about by an open-market operation by the monetary authority. With the new money supply, equilibrium in the money sector can be represented by L’M’ curve in Fig. 6.5.
Demand For Money And Real Interest Rate Definition
At A, the goods sector is still in equilibrium, since nothing has happened to change the IS curve. However at A, the quantity of money supplied is greater than the quantity of money demanded as the situation in the money sector represented by the L’M’ curve. Individuals will be attempting to reallocate their wealth from money into bonds, thus driving the interest down.
The fall in interest rate also affects the goods sector via its effect on desired I; thus point A will not remain an equilibrium point for the goods sector either. The changes in the goods sector thus generated will have repercussions on the money sector. The process will continue until a new equilibrium is reached at point B, at which both sectors are in equilibrium again.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The above discussion shows how changes in one sector of the economy are transmitted to the other sectors, and how the final equilibrium of the whole system is reached. It is obvious that changes occurring in one sector can only be transmitted to another sector if there exist variables linking the two sectors, and if these changes affect these linking variables.
In our model, the linking variables are the interest rate and real Y. The interest rate is an effective linking variable, transmitting changes of behaviour occurring in the money sector to the goods sector, because the change in the money sector had an effect on the interest rate and the interest rate enters in the goods sector through investment decisions.
Real Y is an effective linking variable, transmitting changes of behaviour in the goods sector to the money sector, because changes of behaviour in the goods sector has an effect on real income Y and real Y enters into decision in the money sector through changes in the demand for money.
To get a better idea about these linking variables, we examine the following cases:
i. The Perfectly Elastic Demand for Money or the Liquidity Trap:
We have already seen the interest rate as a measure of the alternative cost of holding wealth in the form of money rather than in the form of other assets and thus, as a measure of the cost of acquiring the services yielded by money. When the interest rate is zero, the cost of acquiring services provided by money is zero and people will be willing to hold all their wealth in the form of money rather than other assets.
It is possible that even when the interest rate is positive, the expected cost of holding wealth in the form of money is zero. We have already seen that one of the costs of holding bonds is the risk of capital loss arising from a change in the interest rate. When the interest rate rises, there would be a fall in the capital value of bonds; the expected return from holding a bond is equal to the interest yield minus the expected capital toss. If these two are equal, the expected final return is still zero, even though the interest yield is positive.
Assume for the moment that the interest rate is considered to be normal, say, rn. If the interest rate falls below rn , individuals expect it to return to rn and thus they expect to suffer a capital loss if they hold bonds. Let rL < rn be the interest rate which would cause capital loss if the interest rate rises from r, to the expected rate rn which exactly offsets the return represented by rL.
In this case, at the interest rate rL, the expected return from holding a bond is zero. At the interest rate above rL, it is positive, and at an interest rate below rL, it is negative. This case is represented by a demand curve for money which becomes perfectly elastic at the interest rate rL in Fig. 6.6.
Fig. 6.6 (a) shows 3 demand curves for money for three different incomes, where Y1 < Y2 < Y3, having the property that at the interest rate rL they become perfectly elastic — at this interest rate people are willing to hold all their wealth in the form of money. Ms1 and Ms2 are two different supply curves of money. In Fig. 6.6 (b), the LM curves are derived to represent this situation. They are perfectly elastic at the interest rate rL for incomes up to Y2 for LM1 and up to Y3 for LM2.
The increase in money supply from Ms1 to MS2 only affects the elastic part of the LM curve, because an increase in the supply of money along the perfectly elastic part of the demand curve for money has no effect on the interest rate. Individuals are willing to hold more money, rather than bonds at rL, where the cost of holding money is zero and individuals are indifferent between money and bonds.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Fig. 6.7 represents a general equilibrium situation for a goods sector represented by IS curve and a money sector exhibiting the properties above, represented by LM, with equilibrium for both sectors on the horizontal part of the LM curve at Ye and rL, respectively. Assume there is an increase in the supply of money shown by a shift of the LM curve from LM1 to LM2. This has no effect on the equilibrium value of real Y or the interest rate because the part of the LM curve affected by this change is not relevant to the determination of equilibrium.
ii. The Supply of Money is Perfectly Elastic:
This happens when the monetary authority decides to fix the interest rate at some given level. To do this, they will have to supply whatever quantity of money is demanded at that rate, otherwise the interest rate would be affected by the excess demand or supply of money and would not be maintained at the desired level. This is shown in Fig. 6.8(a) which shows a supply curve that is perfectly elastic at the interest rate rf and three demand curves for three incomes. In Fig. 6.8(b), we derive the LM curve for this situation. It is perfectly elastic at the interest rate rf. We can see that any changes in the demand for money (or price level) will have no effect on the LM curve.
If we draw the IS curve on the LM curve of Fig. 6.8(b), we have the same general equilibrium situation as the one in Fig. 6.7. Again changes in the demand for money (or price level) will have no effect on equilibrium Y or interest rate. This is the situation which Keynes experienced and thus, he advocated fiscal policy as an effective instrument for influencing the economy.
iii. The Perfectly Inelastic Investment Function:
The IS curve represents all the combinations of income and interest rate at which AD = Total Output. Both the interest rate and real income are relevant here because we assume that both these variables affect decisions about AD; the interest rate affects desired investment and real income affects desired consumption.
If we now drop the assumption that desired investment depends on the interest rate, real Y becomes the only variable that affects AD, and the IS curve in such a situation will be perfectly inelastic. Fig. 6.9 shows such an IS curve with two LM curves representing two different conditions in the money sector (two different supply functions).
With both LM curves, general equilibrium in the two sectors occurs at the same real income but at different interest rates. Thus any changes in the money sector (shifts in the LM curve) only affect the interest rate, but leave real Y unchanged. However, changes in the goods sector (shift of the IS) affect both real Y and the interest rate.
iv. The Real Balance Effect:
The Neo-Classical economists, mainly Prof. Pigou, produced an argument against the Keynesian liquidity trap case in the shape of real balance effect. According to this, with a constant nominal money supply, a general deflation of wages and prices tend to increase the real value of people’s holdings of money above their desired levels.
Consequently, people will reduce their savings and increase their consumption in an attempt to reduce their real balances. In a situation of unemployment, as wages and prices fall and the LM curve shifts to the right, the IS curve will also shift to the right as consumption increases. With both curves now shifting to the right, the equilibrium levels of income and hence employment must increase (even in the liquidity trap and with interest-inelastic investment) and there is now nothing to stop full employment from being reached. This is illustrated in Fig. 6.10.
Theoretically, then, the neo-classical economists appear to have the stronger case. Only when it came to policy-making, did the Keynesians have the upper hand, given the recognised inflexibility of wages and prices downward.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The cases examined here are important in showing, how, by changing assumptions about behaviour; the inter-relationship between the two sectors is changed. In the first two cases, we still assume that there is a linking variable between the goods and money sectors; desired investment is assumed to be a function of the interest rate.
However, the assumptions about the money sector are such that any changes in this sector do not affect the linking variable (the interest rate) and thus such changes are not transmitted in the goods sector. In the case of the assumption about a perfectly inelastic investment function, the goods sector is totally independent of the money sector — no behaviour in the goods sector is affected by the money sector.
Even if changes in the money sector affect the interest rate, it is unlikely to affect the goods sector so long as the interest rate plays no role in any behaviour relevant to that sector. (If consumption is a function of interest rate, this would reintroduce a link between the goods and the money sectors even though desired investment is not a function of the interest rate). However, changes in the goods sector do affect the money sector, because the variable linking the two – real income — is effective as long as the demand for money is a function of real income which may change because of the real balance effective.
A Formal Treatment of the IS-LM Model:
Equilibrium Income and the Interest Rate:
The intersection of the IS and LM curves determines equilibrium income and interest rate. We derive expressions for these values by using the equations of IS and LM curves.
Modern Monetary Theory:Keynes argued that there were three reasons for holding money:
1. Transactions motive
2. Precautionary motive

3. Speculative motive - holdings of money as a wealth asset
The idea behind the speculative motive is that individuals will shift their wealth between liquid and illiquid assets, i.e.,
between money and bonds or stocks, as the interest rate changes.
For this reason, Keynes called the demand for money liquidity preference.
The liquidity preference function says that the demand for money depends on both the level of real GDP and on the
rate of interest. We will write it as a linear function, and we will express money as real balances, that is, we will look
at the purchasing power of the amount of money demanded. So, real balances are M1/P.
[M1/P]D = demand for real money balances
= L(r,Y) = f*r - g*Y f>0, 0<g<1
On a diagram, with the interest rate on the vertical axis and real money balances on the horizontal, the demand for money,
or liquidity preference, function is a downward sloping curve.
Each new value of Y will generate a new liquidity preference line.
The basic behavioral assumptions about the demand for money are that individual wealth holders want to avoid capital losses, and that all gains and losses, in the simple model, depend on expected interest rates. If rates fall, the capital market value of assets like bonds will rise, and if rates rise, the capital market value of assets like bonds will fall.
For convenience, for now, we will assume that the only interest bearing assets in the economy are bonds. Thus, in the simple case we are discussing, individual wealth holders can hold real money balances, which do not bear interest, and bonds, which do bear interest. [In reality, of course, there are assets that earn a return; time deposits, bonds, stock shares, etc.]

If real interest rates in the economy fall, individual bond holders will want to hold more real money balances and fewer bonds; they will want to sell their bonds, make capital gains, and then hold money. Falling interest rates mean that money is cheaper to hold, ie., has a lower opportunity cost.
If interest rates in the economy rise, individual bond-holders will want to buy bonds, which are getting cheaper, and hold less real money balances; the opportunity cost of holding money has risen.
In a more complicated model, with many types of assets earning a return, individuals will adjust the portfolio of wealth holdings, and not just the money versus bonds decision. If the interest rate structure changes, individuals may move their wealth around from stocks to bonds to mutual funds to savings accounts to real balances.
Demand For Money And Real Interest Rate Include
At his point, Keynesian theory has to address the problem of interest rate determination. In classical models like Fisher's the interest rate is determined in the market for loanable funds, i.e., at the intersection of the investment and savings functions. But, as we saw earlier, Keynes argued that savings does not depend on the interest rate. So, he argued that the intersection of the supply and demand for money determined the interest rate.
Thus, in the Keynesian model, a change in either the nominal money supply (M1) or the price level (P)
will cause the rate of interest to change.
Further, a change in M1 will cause a change in the rate of interest, that will then affect aggregate expenditure
by causing the level of investment, or the level of autonomous consumption to change.
We can show this be examining how monetary. We will use a money market graph, a
graph of Autonomous Spending with respect to the rate of interest, and the Aggregate Expenditure graph.
Money Demand And Real Interest Rate
Monetary Policy: When the money supply increases, M1 rising to M'1, the interest rate will fall (Point E to point F in the left diagram).
This will cause Autonomous Spending to rise, (Point E to point F in the right diagram.) That will cause AE to rise, and then real GDP to rise, through the
multiplier process (Point E to point F in the bottom diagram.) [For practice, draw the results in the AD-SAS diagram. How will the increase in AE
above affect AD?]
Thus, changes in the money supply will affect real output, through changes in the interest rate.
Economists argue about the relative strength of various parameter shifts. How elastic is the liquidity preference function and
the aggregate expenditure function with respect to the interest rate?
Monetarist: The liquidity preference function is relatively inelastic, and the aggregate expenditure function is relatively elastic,
with respect to the interest rate. Short run AS is steep, but not vertical.
Keynesian: The liquidity preference function is relatively elastic, the aggregate expenditure function is relatively inelastic with respect
to the interest rate. Short run AS is not very steep.
Rational Expectations point of view: Individuals collect the best available information and act on it rationally. Wages and prices are flexible and adjust quickly. Therefore, the Classical model makes sense. We will only get involuntary unemployment if individuals mis-read available information (make mistakes) or if they do not realize what is happening. Fiscal and monetary policy will be ineffective since actors in the economy will anticipate perfectly what the policy response will be to any change, and will neutralize it. GDP will always be at its potential or natural level, i.e., the AS curve is vertical. We should rely on consistent, long-run policy rules to run the economy and to provide individuals with good information about what to expect.
KEYNESIANS AND MONETARISTS
1. Keynesians believe more strongly in fiscal policy, and Monetarists believe more strongly in monetary policy.
2. Policy lags are shorter for monetary policy than for fiscal policy, but monetary policy usually takes longer to work on the economy. Changes in G and Tx work quickly on the economy, once they are made. Friedman says monetary policy lags are 2 to 6 months. Fiscal policy can take a long time, since Congress must act on it. Automatic Stabilizers are fiscal policy tools that take effect as needed, with no Congressional or Presidential action.
Demand For Money And Real Interest Rates
3. Keynesians believe the FED should control the rate of interest. Monetarists believe the FED should keep the money supply growing at a stable, if not constant, rate.
PROBLEM: If money demand shifts out autonomously, then r and M1
will both rise, if the money supply is upward sloping. In such a case, the FED cannot control both r and M1. If the demand for money jumps around erratically, control of the supply of money is almost impossible. M1 must be adjusted to compensate for fluctations in r caused by the jumping-around of money demand. The FED must always consider that higher r may dampen investment and consumption, but the drop in investment spending may have serious long-run effects. The growth of the economy will slow if investment stays depressed.
4. Keynesians believe the short-run aggregate supply curve is relatively elastic [flat]. Monetarists believe the short-run aggregate supply curve is relatively inelastic [steep].
5. Keynesians believe that discretionary stabilization policies, both fiscal and monetary, are desireable. They are not convinced that economy will operate well on its own. Monetarists believe that lags and uncertainties make any form of discretionary stabilization policy very difficult, if not counter-productive. They believe the economy, if left to its own devises, operates quite well. Therefore, Monetarists believe in policy rules, and Keynesians believe in discretion.